Introduction: More Than Just a Mobile Wallet
M-PESA isn't just a mobile money service; it's a financial ecosystem that has transformed economies, particularly in Kenya where it launched in 2007. To many users, it appears simple: send money, pay bills, and save funds through a basic mobile phone interface. But beneath this straightforward user experience lies a remarkably complex, secure, and highly orchestrated digital infrastructure.
This deep-dive explores the intricate machinery behind M-PESA—the technological architecture, the agent network logistics, the financial settlement systems, and the regulatory frameworks that allow millions of transactions to flow securely every single day. Understanding how M-PESA truly works reveals not just a technical marvel, but a blueprint for inclusive digital finance.
The Foundational Concept: Leveraging SIM Card Real Estate
At its core, M-PESA is a SIM-based application. Unlike smartphone apps that reside in phone memory, M-PESA was originally designed for feature phones and operates using SIM Toolkit (STK) technology. When a user subscribes to M-PESA, their mobile network operator (like Safaricom in Kenya) provisions a dedicated space on their SIM card. This space hosts a secure, menu-driven application that is accessible even without mobile data, using Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD) codes, most commonly *234#.
This choice of technology was deliberate and revolutionary. By using USSD—a protocol already built into all GSM phones for checking balances or topping up airtime—M-PESA became instantly accessible to the entire population, not just smartphone owners. The USSD session creates a real-time, encrypted connection between the phone and the core M-PESA system, allowing users to navigate menus and input transaction details securely.
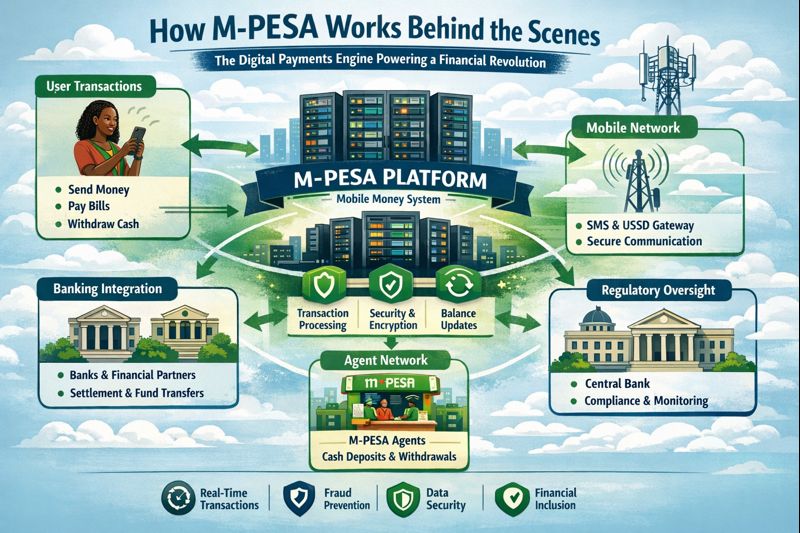
The Three-Tiered Architecture: A Symphony of Systems
Behind the USSD menu is a sophisticated, multi-layered technical architecture designed for resilience, security, and massive scale.
1. The Front-End: USSD Gateway and Mobile Network Integration
When a user dials *234#, the request hits the mobile carrier's USSD gateway. This gateway routes the session to the M-PESA platform, not as a voice call, but as a data packet. The gateway manages session persistence—keeping the connection alive as the user navigates menus—and handles the initial encryption. It's also responsible for user authentication, confirming the phone number initiating the session matches the registered M-PESA account.
2. The Core Engine: The M-PESA Platform Vault
This is the beating heart of the system—a centralized, high-availability server cluster often running on robust, fault-tolerant systems from providers like Oracle or IBM. This "vault" maintains the definitive ledger of all M-PESA accounts. Crucially, it doesn't store actual Kenyan shillings; it stores electronic value.
Each account has an e-value balance, a digital representation of money held in trust by Safaricom in regulated bank accounts. The platform processes transaction logic: debiting one account, crediting another, validating sufficient funds, and applying transaction fees. It generates the real-time SMS receipts that are M-PESA's hallmark and enforces transaction limits set by regulators.
3. The Back-End: Integration and Settlement Layer
This layer connects M-PESA to the wider world. It includes:
Banks: Via secure APIs and financial messaging (like ISO 8583), it allows for bank-to-M-PESA deposits and withdrawals.
Merchants: Enables Lipa Na M-PESA (Pay with M-PESA) by connecting to merchant payment gateways.
Utility Companies: For bill payments.
Settlement System: The most critical back-end component. At the end of each day, the net positions of all transactions must be settled in real, central bank money. This involves calculating the net movement of funds between Safaricom's trust accounts at commercial banks and the accounts of banks, utility companies, and other large partners.
The Agent Network: The Physical Bridge to Cash
The digital system would be useless without a way to convert physical cash to electronic value and back. This is the role of the vast agent network, the human and physical infrastructure that gives M-PESA its tangible presence.
Agent Mechanics: E-Value Inventory Management
An agent isn't just a shopkeeper with extra cash. They operate a dedicated M-PESA till, often a special phone or tablet. To become an agent, they must deposit a float—real cash—into a designated commercial bank account. This cash is converted into an equivalent amount of e-float in their agent account on the M-PESA platform.
When a customer wants to deposit cash (Cash-In), the agent collects the physical cash and, via their agent menu, transfers e-float from their own agent account to the customer's personal M-PESA account. The agent's physical cash increases, and their e-float decreases. The reverse happens for Cash-Out: the agent gives the customer physical cash and receives e-float from the customer's account.
Liquidity Management: The Daily Dance
A successful agent must dynamically manage two balances: physical cash and e-float. An agent who runs out of cash cannot serve customers wanting withdrawals; an agent who runs out of e-float cannot accept deposits. This creates a local market.
Agents often buy and sell e-float amongst themselves via an internal settlement system called SokoSoko to rebalance. Super-agents and aggregators provide larger-scale liquidity services, moving large amounts of cash and e-float to maintain equilibrium across the network.
The Trust Account Model: Where the "Real" Money Lives
A fundamental question for any user is: "Is my money safe?" The answer lies in the safeguarding trust account structure, mandated by the central bank.
Safaricom does not commingle M-PESA customer funds with its own operational capital. All customer e-value is backed 100% by real Kenyan shillings held in pooled trust accounts at one or more licensed commercial banks (like the National Bank of Kenya). These are ring-fenced accounts, meaning they are legally protected and cannot be accessed by Safaricom's creditors. The total balance across all user M-PESA accounts must always equal the total sum held in these trust accounts. Regulators conduct frequent audits to ensure this parity.
When you send 100 KSh to a friend, no physical money moves instantly. Your e-value balance decreases by 100, theirs increases by 100. The underlying cash remains in the trust account. Only when your friend cashes out at an agent does the chain complete: the agent gives them physical cash, the agent's e-float is reduced, and the net settlement process at the end of the day will eventually move funds from Safaricom's trust account to the bank account of the agent's aggregator to replenish the agent's cash float.
The Settlement Engine: Resolving the Money Trail Daily
While customer transactions feel instantaneous, the final movement of sovereign currency between institutions happens in batches. The end-of-day settlement is a critical behind-the-scenes process.
Transaction Aggregation: The M-PESA platform aggregates all transactions from the day, categorizing them: Customer-to-Customer (C2C), Cash-Ins, Cash-Outs, Bank Transfers, Merchant Payments, etc.
Net Position Calculation: For each participating entity (each bank, large merchant, utility company, and the agent network aggregators), the system calculates the net position. Did more money flow from their customers into M-PESA than out? If so, they are owed money. Did more flow out? Then they owe money.
Central Bank Settlement: These net obligations are settled through Kenya's Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) system, operated by the Central Bank of Kenya. Large-value transfers move between the commercial bank accounts of the involved parties, ultimately ensuring the trust account balances accurately reflect the e-value in circulation.
Agent Settlement: At the agent level, settlement is more frequent, often real-time or daily. The aggregator's system tracks each agent's e-float vs. cash movements and provides them with a statement, facilitating profit calculation (based on commission) and liquidity planning.
Security: The Multi-Layered Fortress
Handling billions of dollars requires military-grade security. M-PESA employs a defense-in-depth strategy:
PIN Encryption: Your 4-digit PIN is encrypted on your SIM card using 3DES or AES standards and is never transmitted in the clear.
Session Security: Each USSD session is encrypted and given a unique transaction ID to prevent replay attacks.
System-Level Security: The core platform is housed in highly secure data centers with biometric access, intrusion detection systems, and 24/7 monitoring.
Fraud Detection Engines: Advanced systems use rules and machine learning to detect anomalous transaction patterns (e.g., sudden large transfers, rapid succession of transactions) and can trigger holds or alerts.
Agent Oversight: Agent transactions are monitored for laundering patterns, and stringent "Know Your Customer" (KYC) rules are enforced during customer registration, requiring a national ID.
The Evolution: APIs and the Platform Economy
The original M-PESA was a closed system. Its modern incarnation is an open platform. Through a suite of secure Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), businesses can integrate M-PESA directly into their operations.
Business to Customer (B2C) API: Allows companies to make bulk payments (salaries, refunds) directly to M-PESA wallets.
Customer to Business (C2B) API: Enables online and in-store payments via Lipa Na M-PESA, with real-time confirmation.
Transactional APIs: Allow developers to build applications for checking balances, transaction status, and account verification into third-party apps.
This API layer has spawned an entire fintech ecosystem, enabling everything from e-commerce checkouts and ride-hailing payments to sophisticated savings and lending products like M-Shwari and KCB M-PESA, which use M-PESA transaction history as a basis for credit scoring.
Conclusion: A Blueprint for Inclusive Finance
Peering behind the scenes of M-PESA reveals a masterpiece of pragmatic engineering, financial architecture, and human-centric design. It is not one technology but a carefully woven tapestry of:
Accessible Tech (USSD/SIM Toolkit) to include everyone.
Robust Core Banking Systems to ensure security and accuracy.
A Human Agent Network to bridge the digital-physical divide.
Strong Regulatory Frameworks to build and maintain trust.
Open APIs to foster innovation on the platform.
The genius of M-PESA is that it abstracts all this immense complexity away from the user, who experiences only simplicity: a few keystrokes on a basic phone to move money. By solving the intricate problems of trust, cash conversion, and settlement behind the scenes, M-PESA has not just created a mobile wallet; it has built a new, inclusive financial infrastructure that empowers millions, proving that the most impactful technologies are those that hide their complexity in service of profound simplicity.